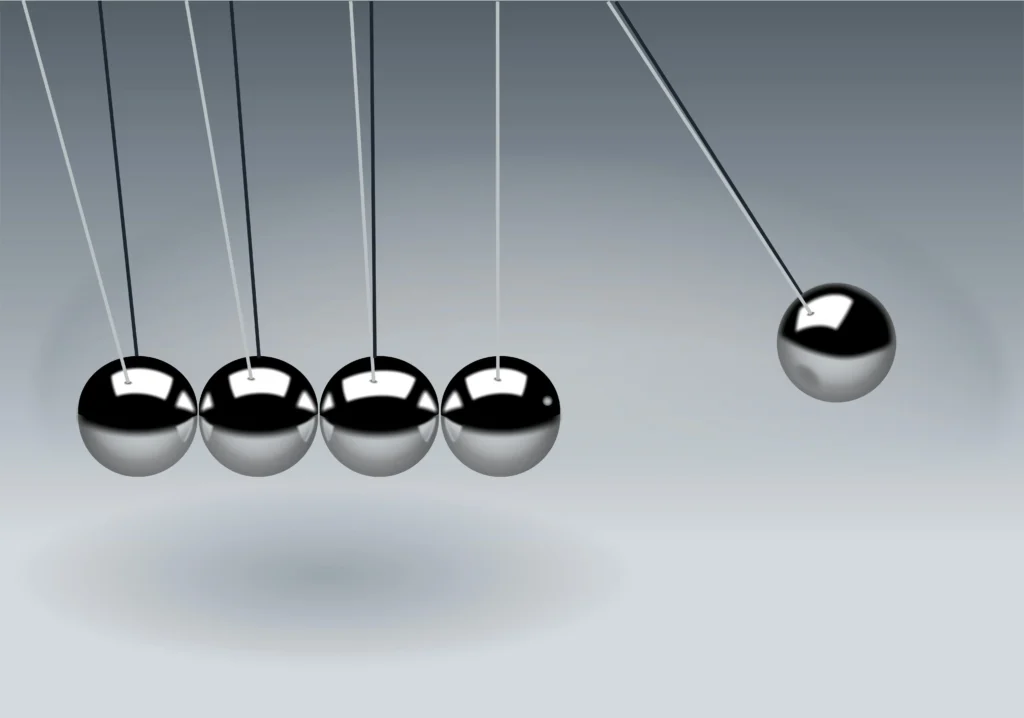
Mechanical energy is the energy contained by an object because it is moving or in some place. It is the combination of two energies:
- Kinetic energy (energy of motion)
- Potential energy (stored energy by position)
If it is in motion or has the ability to move, it has mechanical energy. It is the energy responsible for making everything move, fall, rotate, or get pushed or pulled.

Formula of Mechanical Energy
An object’s mechanical energy (ME) is the total of its kinetic and potential energies:
ME = KE + PE Mechanical Energy = Kinetic Energy + Potential Energy
Where:
- KE = ½ × m × v²
- PE = m × g × h
- m = mass of the object
- v = velocity (speed)
- g = gravitational acceleration (9.8 m/s²)
- h = height above the ground
By calculating and adding the two types of energy, one can determine the total mechanical energy of an object at a height and in motion.
Examples of Mechanical Energy
- A moving car
- A stretched bow before releasing an arrow
- Above a hill, a roller coaster
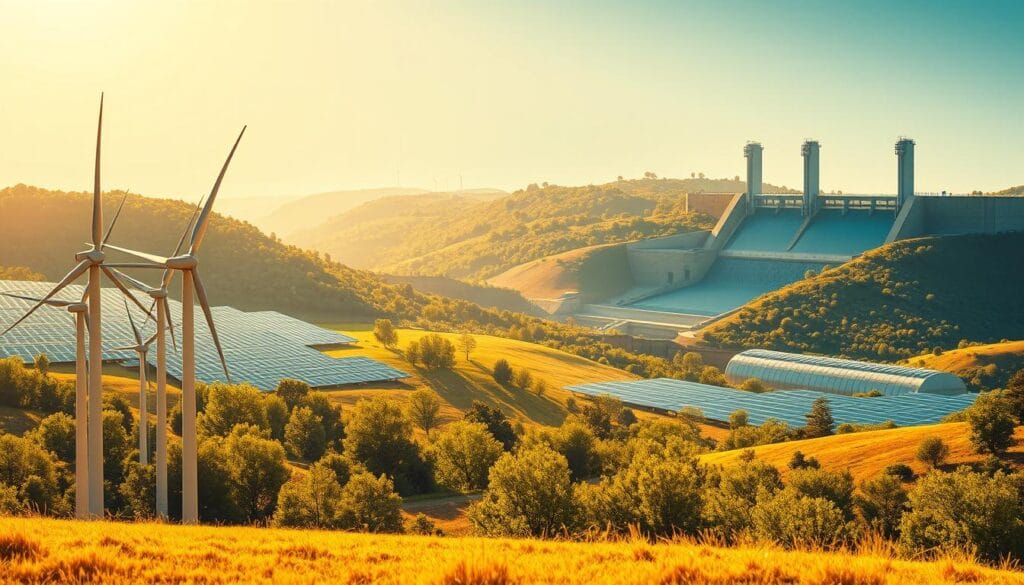
- Wind turning a windmill
- Water stored behind a dam and then released
These examples are all related to mechanical energy because they all involve movement, the capacity to move, or both.
Is mechanical energy potential or kinetic?
Mechanical energy is potential and kinetic energy combined. Potential energy is within an object due to it existing in a location (like an elevated weight), while kinetic energy is the energy within a moving object (like a traveling car).
Therefore, mechanical energy can be either or both, depending on whether an object is moving, ready to move, or both.
References
The information in this article is based on insights from respected organizations in the energy field. We have reviewed content from the following sources to ensure accuracy and relevance:
Posted by Abu Talha
With a background in science at the A-level, Abu Talha has studied subjects including physics, chemistry, mathematics, and biology. Along with his more than 1.5 years of experience in digital marketing, he is passionate about writing about electric vehicles, sustainable energy, and how emerging technologies are influencing the future.