Hydropower is the production of electricity from the natural movement of water. Also simply referred to as hydroelectric power, it is a clean and renewable energy source that has been around for more than a century.

What makes hydropower so valuable is that it is versatile. It can quickly adjust to changing electricity needs, and it is the perfect balance to other renewable sources like solar and wind. As the weather changes, hydropower is there to keep the balance.
Examples of Hydropower
Large-scale hydropower systems fall into three general categories: impoundment, pumped storage, and diversion. They differ slightly in their operation but all utilize the kinetic energy of moving water to produce electricity.
Impoundment
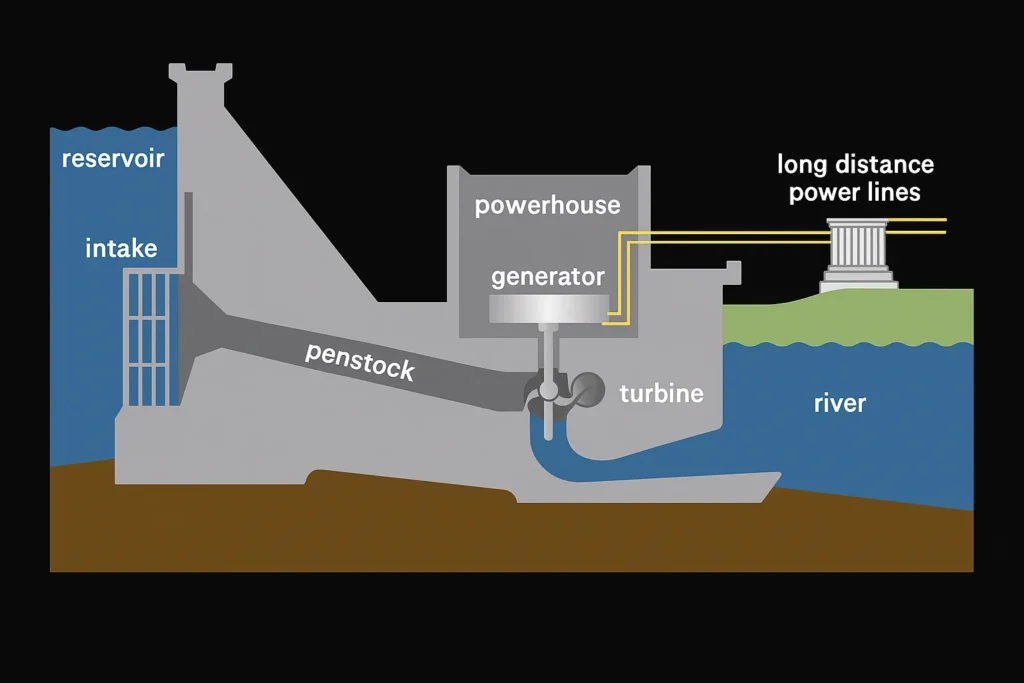
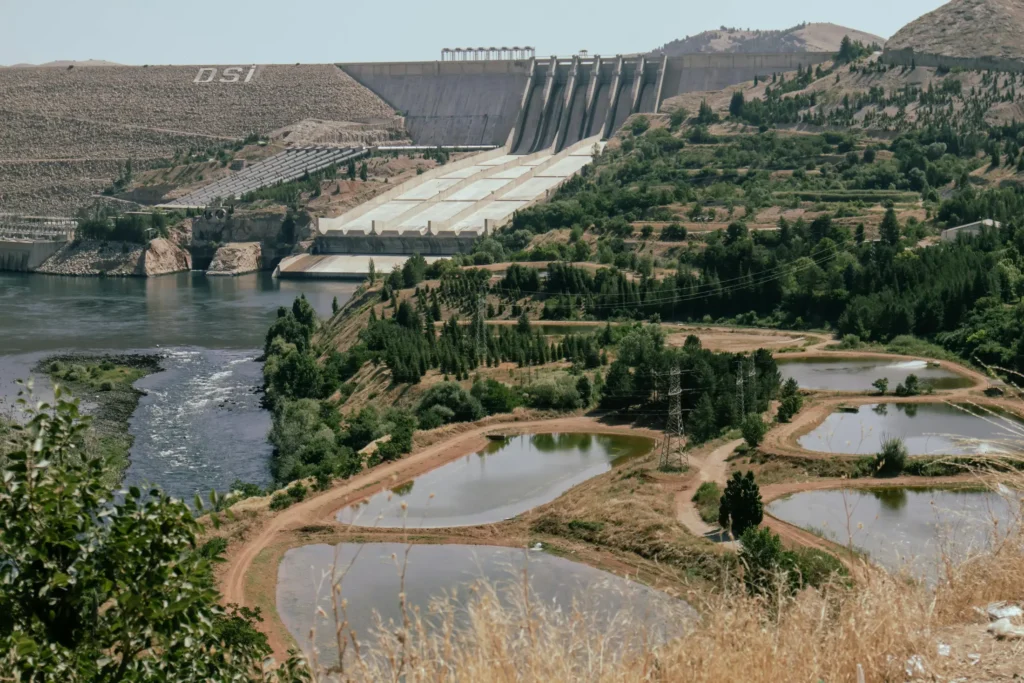
This is the most typical way that hydropower is used. It entails constructing a dam to store a lot of water. Water is released through turbines inside the dam when electricity is required. When the water passes through these turbines, it makes them rotate and thus generate electricity.
The Hoover Dam is among the most well-known examples of this phenomenon. Most contemporary impoundment dams today incorporate aspects such as fishways to minimize their environmental footprint.
Diversion
Most commonly known as a run-of-river system, this configuration diverts part of a river’s flow without the use of a large dam. Water is channeled through a pipe or conduit called a penstock, where it flows through turbines to generate electrical power.
After it goes through, the water returns to the river. Since it does not block the entire stream, this type is generally considered more environmentally friendly.
Pumped Storage
This cycle works like a huge energy storage system. During low electricity demand, water is pumped from a lower reservoir to an upper reservoir using energy obtained from non-conventional sources like wind power or nuclear power.
When the demand later increases, the water is permitted to flow back downwards through turbines, producing electricity in the process. It is inexpensive and assists in grid balancing, but with a greater environmental footprint than any other type.
I hope this helped you understand the true meaning of hydropower.
Posted by Abu Talha
With a background in science at the A-level, Abu Talha has studied subjects including physics, chemistry, mathematics, and biology. Along with his more than 1.5 years of experience in digital marketing, he is passionate about writing about electric vehicles, sustainable energy, and how emerging technologies are influencing the future.