Biomass energy is one type of renewable energy that derives from organic matter — primarily plants and animals.

These materials, commonly called biomass feedstocks, capture sunlight by means of photosynthesis. When we process them into usable energy forms such as heat, electricity, or fuel, we release that stored energy.
This type of energy is increasingly important as the globe departs from fossil fuel sources such as coal, oil, and natural gas. Biomass provides a sustainable solution, particularly to generate electricity, provide heat, or create cleaner fuels for use in transportation.
Where Does Biomass Originate?
Biomass energy utilizes a variety of organic materials. Among the most accessible resources are:
- Wood waste: logs, wood chips, sawdust, and wood pellets, for example.
- Crop residues: For example, sugarcane bagasse, corn stalks, and wheat straw
- Animal manure and livestock waste
- Food waste and household and commercial biodegradable trash
- Urban municipal solid waste (MSW)
- Algae and aquatic vegetation
- High-yielding energy crops such as miscanthus and switchgrass
- Landscaping debris, grass clippings, and garden trimmings
- Industrial residue, such as paper pulp
The fact that most of these materials can naturally regenerate or be replaced makes biomass renewable. Even food waste and grass cuttings — which are produced by everyday human activity — can be harvested and reused to generate energy.
Why Is Biomass Considered Renewable?
While it takes millions of years to produce fossil fuels, biomass can be produced, grown, and used quickly. Greenery develops, sequesters carbon dioxide, and gets replanted. Animals give off waste all the time. Organic waste is produced every day. If we only handle resources with care, biomass will never deplete.
This cycle — growing plants, using them for energy, and then growing them again — makes it possible for biomass to be a renewable component of our energy mix.
How Is Biomass Used?
Biomass energy is used in several ways:
- Direct heating: Combustion of wood or organic matter to warm houses or industrial plants.
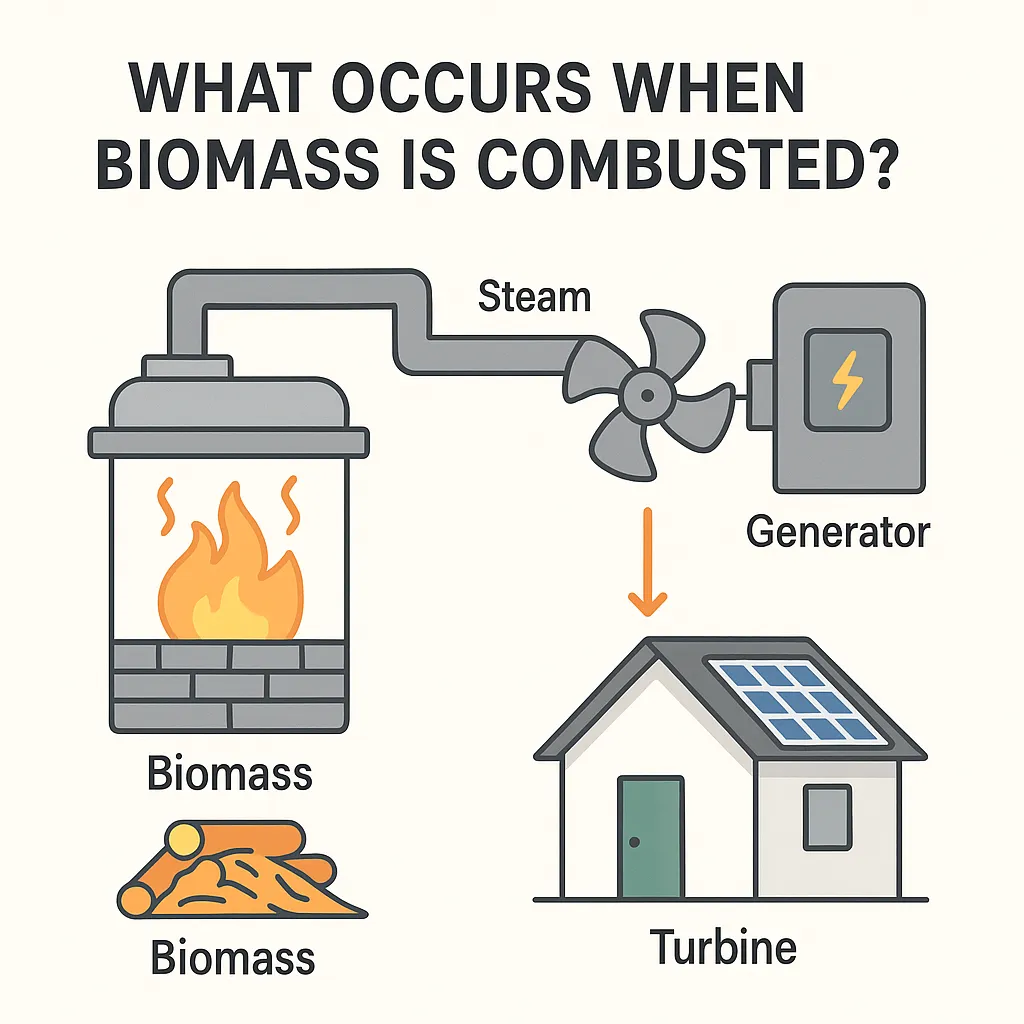
- Electricity generation: Turbines are powered by steam created when biomass is burned.
- Biofuels: Refining plant material to liquid fuels such as ethanol or biodiesel, for use in vehicles.
Each of these applications contributes to decreased dependence on fossil fuels and minimizes greenhouse gas emissions when properly managed.
Summary
So, what is biomass energy? It is energy contained in common organic matter — from tree limbs and agricultural waste to algae and food wastes. As long as we continue to cultivate plants, process waste, and generate renewable resources, biomass will be an available and renewable means of producing energy.
It is not about substituting fossil fuels — it is about making better use of what we already have, and doing so in a way that’s more kind to the planet.
In my opinion, biomass energy provides a workable substitute in situations where resources are scarce. I have witnessed the advantages of basic biomass systems for nearby communities.
Posted by Abu Talha
With a background in science at the A-level, Abu Talha has studied subjects including physics, chemistry, mathematics, and biology. Along with his more than 1.5 years of experience in digital marketing, he is passionate about writing about electric vehicles, sustainable energy, and how emerging technologies are influencing the future.