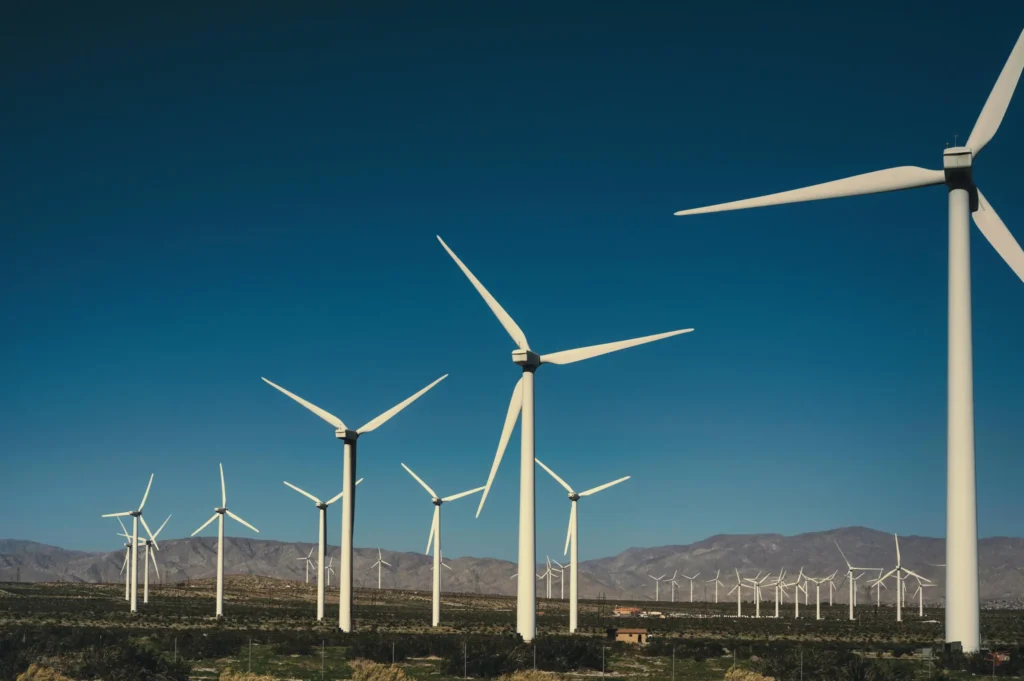
Wind energy works on the principle of employing large blades which harness the kinetic energy of moving air and generate electricity. When it is windy, it causes the turbine blades to rotate. That rotation results in a shaft connected to a generator, and that powers electricity.
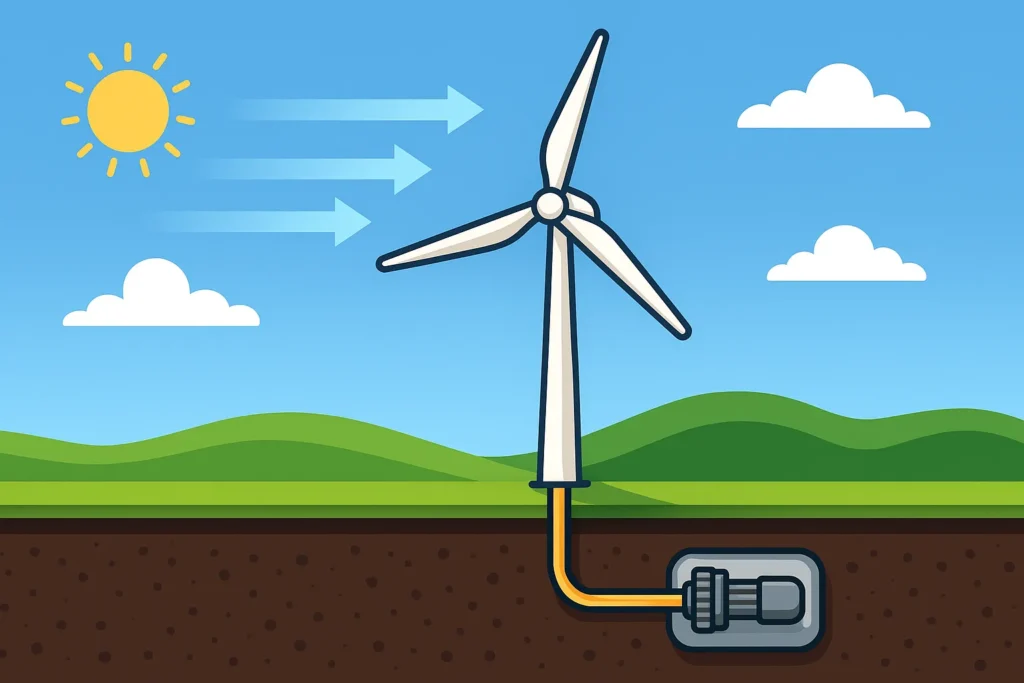
The method is clean and not fossil fuel-based, and hence it is one of the most sustainable forms of energy currently.
Wind: A Form of Solar Energy
Wind energy is actually a result of solar energy. It forms due to three natural phenomena working together:
- Inequalities in Heating of the Earth’s Surface by the Sun – The different parts of the Earth receive solar energy unequally.
- Irregular Surface Features of the Planet – Mountains, valley, and water bodies influence the way air moves.
- Earth rotation – As it turns, the Earth affects the velocity and direction of the wind.
These forces make air move, which we refer to as wind. Wind turbines use this motion to produce electricity.
Main Types of Wind Turbines
There are two most significant forms of wind turbines, based on their blade orientation:
1. Horizontal-Axis Wind Turbines
These are the most common type. They resemble airplane propellers in that their blades rotate on a horizontal axis. Typically, they are affixed to tall towers in order to be nearer the more powerful winds.

2. Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines
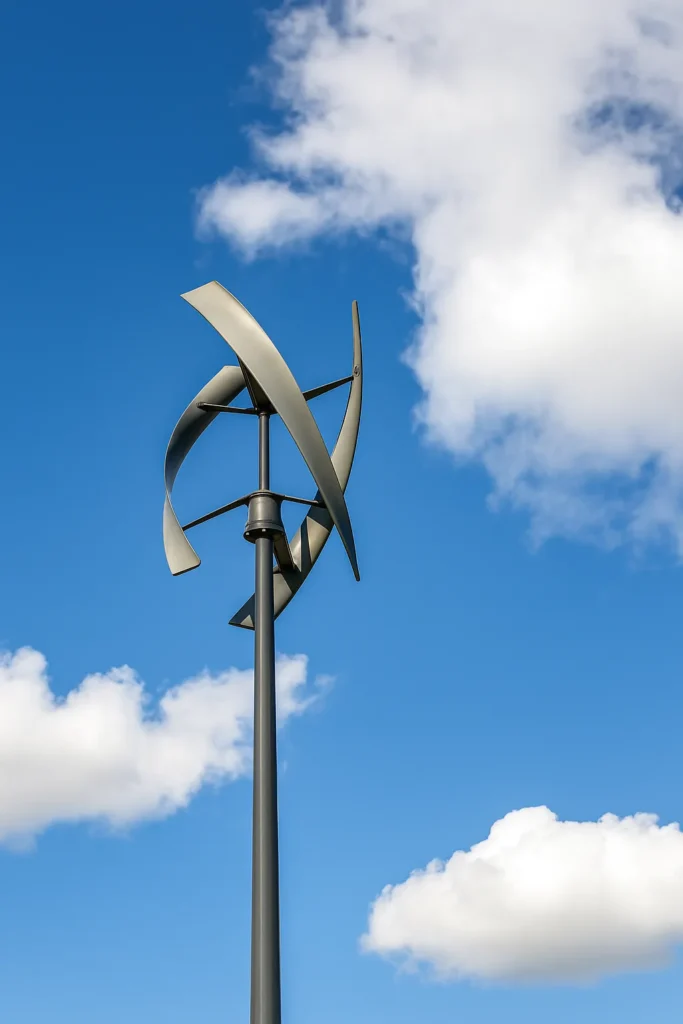

The turbines rotate on a vertical axis such that they can pick up winds from any direction. They are not as efficient but are useful where wind directions vary.
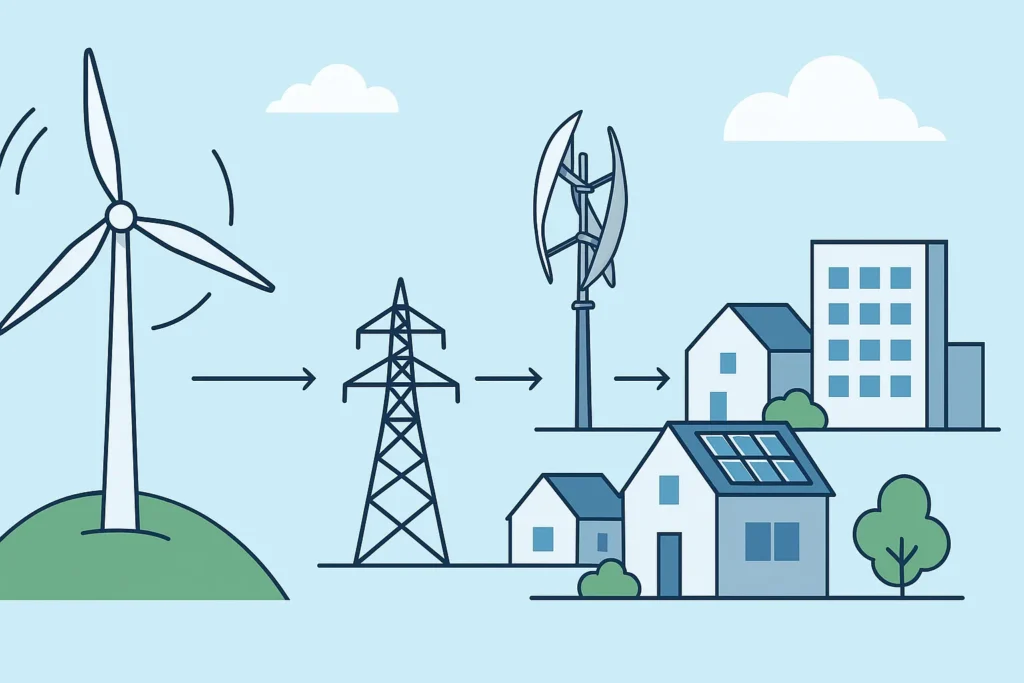
Where Are Wind Turbines Used?
Wind turbines can be mounted in different environments. The three broad applications are as follows:
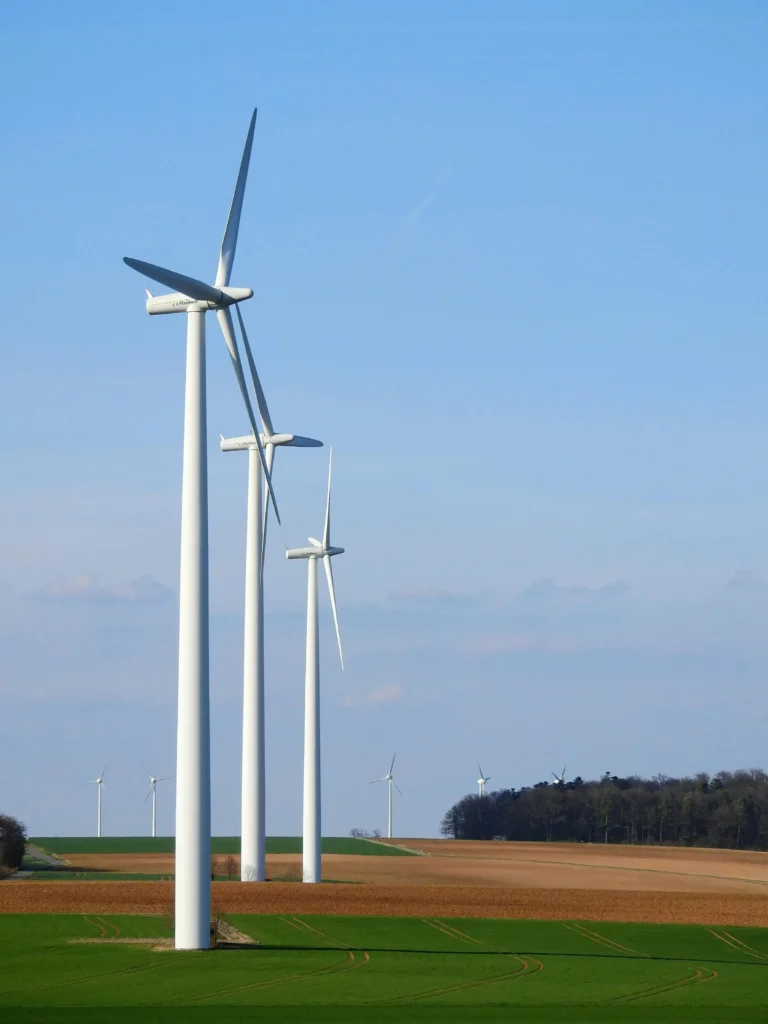
1. Land-Based Wind Farms
These are installed on land in open fields. They are the most widely used and reasonably priced form of wind energy production.

2. Offshore Wind Turbines
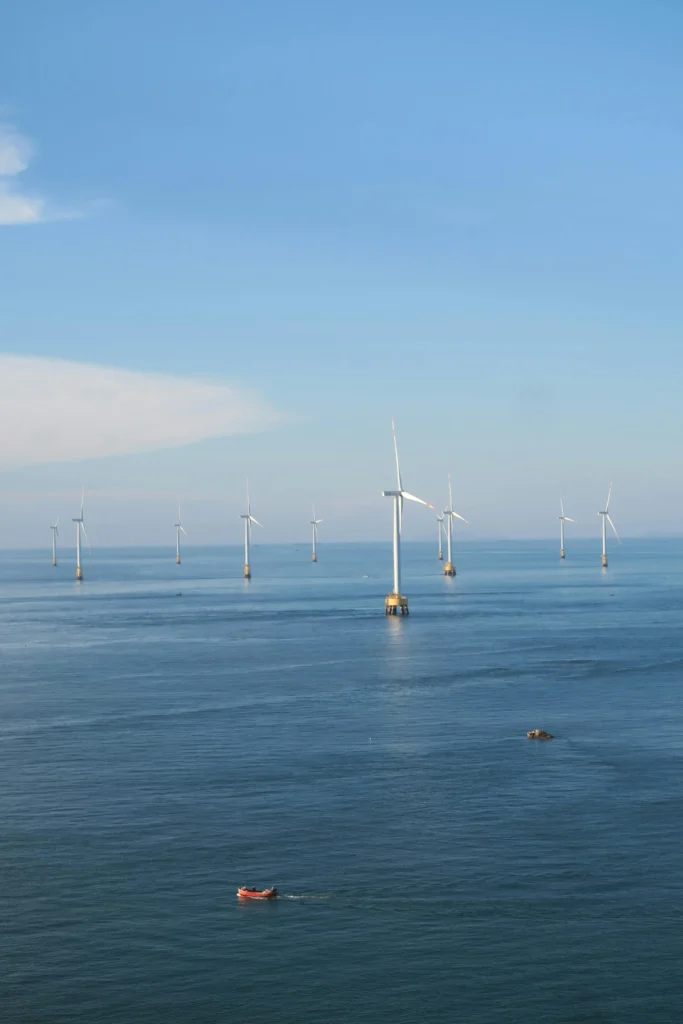

Offshore Wind Turbines Placed in oceans or seas, the turbines utilize constant and powerful sea breezes. They are costly to invest in but produce more power.
3. Distributed Wind Systems
These small turbines are installed near where the electricity will be used—such as homes, farms, or small markets—demonstrating the localized, independent generation of electricity.
FAQs
Q: Why is wind energy environmentally friendly?
Ans: Wind electricity produces electricity without emitting greenhouse gases or other pollutants. It does not require water to cool it and creates no waste.
Q: Can wind turbines operate without wind?
Ans: No. Turbines need a minimum wind speed (usually 6–9 mph) before electricity is produced.
Q: How long do wind turbines last?
Ans: With proper maintenance, wind turbines generally last for 20 to 25 years.
Reference:
- U.S. Department of Energy (energy.gov)
- National Grid Group
- International Renewable Energy Agency
- Queensland Government
- U.S. Information Administration
Posted by Abu Talha
With a background in science at the A-level, Abu Talha has studied subjects including physics, chemistry, mathematics, and biology. Along with his more than 1.5 years of experience in digital marketing, he is passionate about writing about electric vehicles, sustainable energy, and how emerging technologies are influencing the future.

