Let us begin with an easy question: how is biomass energy actually generated from organic waste?
Biomass energy is derived from plant and animal matter — wood chips, crop residue, and even poop. These materials hold energy from the sun, and when we harvest it through various processes, the stored energy turns into usable heat, electricity, or fuel. Let us go through the primary methods it occurs.
What occurs when Biomass is Combusted?
One of the simplest ways is burning biomass. This is referred to as direct combustion.
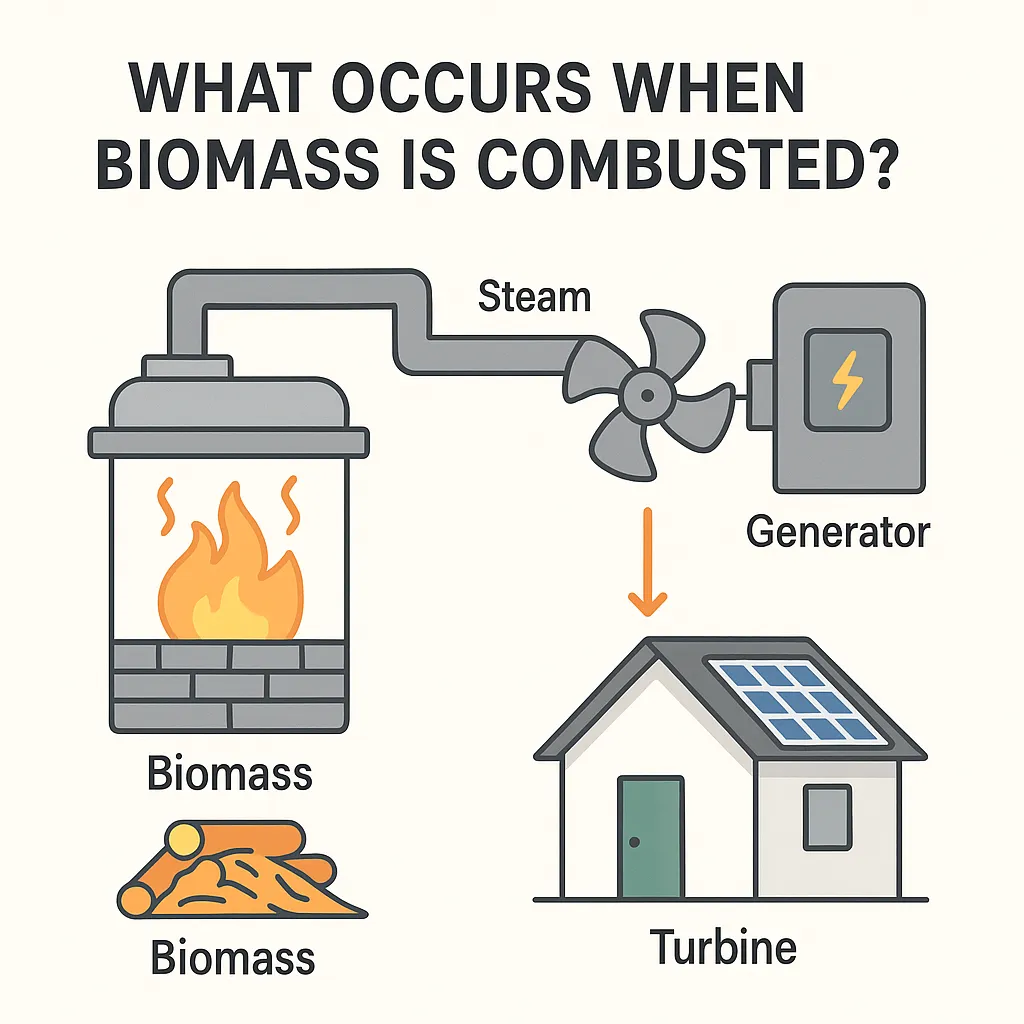
Imagine burning wood in a fireplace — but on a much, much larger scale. When crop waste, wood, or other types of vegetation are combusted, they emit heat. That heat heats water, which creates steam. Electricity is generated by a turbine that is driven by steam.
This is a decades-old process and one that is still widely practiced, particularly where both heat and power are desired in industrial environments.
Can Biomass Be Converted to Fuel Without Burning?
Yes — and that is when thermal conversion is used. In this technique, heat is applied to convert biomass into solid, liquid, or gas fuels but without the simple burning. There are several variations on how to do this:
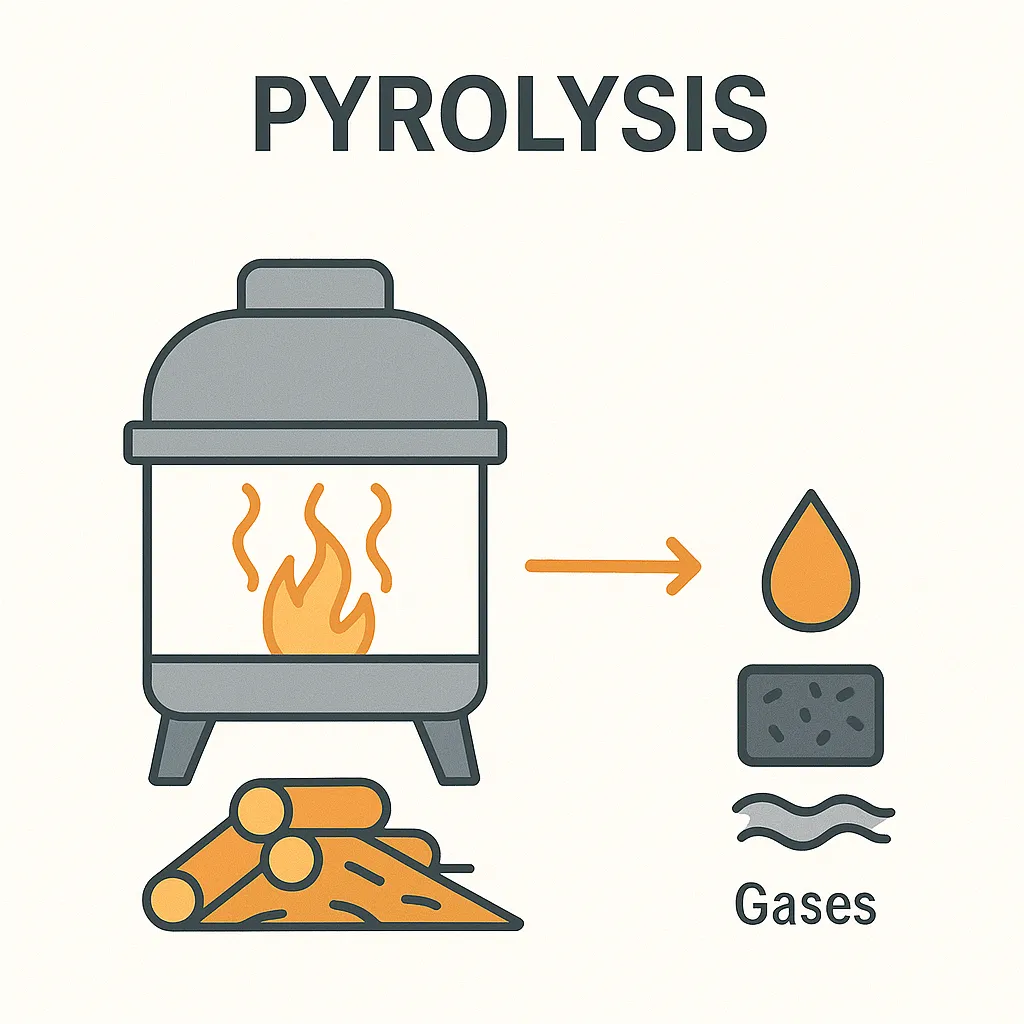
Pyrolysis
The process of pyrolysis involves heating biomass without the presence of oxygen. The material gets broken down into valuable byproducts such as bio-oil, charcoal, and gases like hydrogen and methane. Since there is no oxygen, the material does not burn — it breaks down.
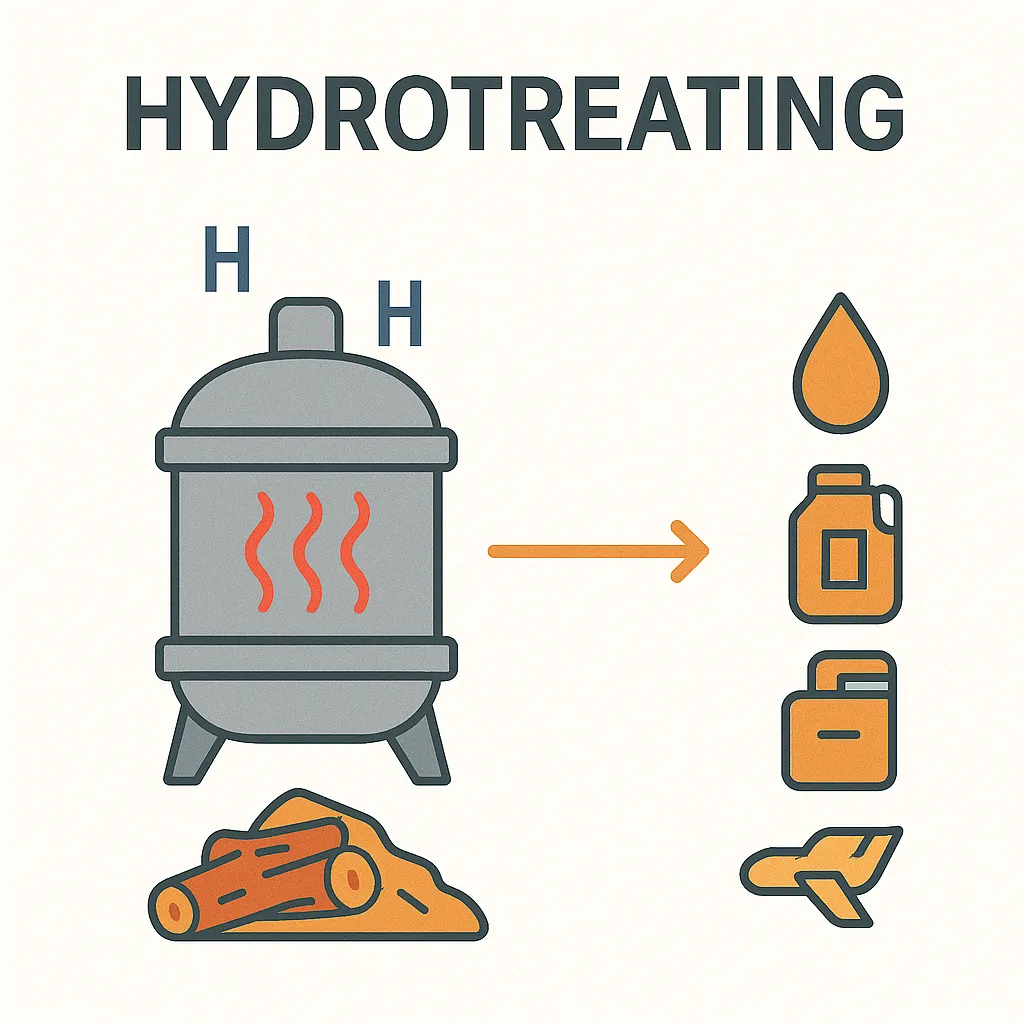
Hydrotreating
This process is similar to pyrolysis but quicker and more powerful.
By introducing hydrogen and subjecting it to high temperature and pressure, we can convert biomass into liquid fuels that are renewable forms — such as diesel, gasoline, and jet fuel.
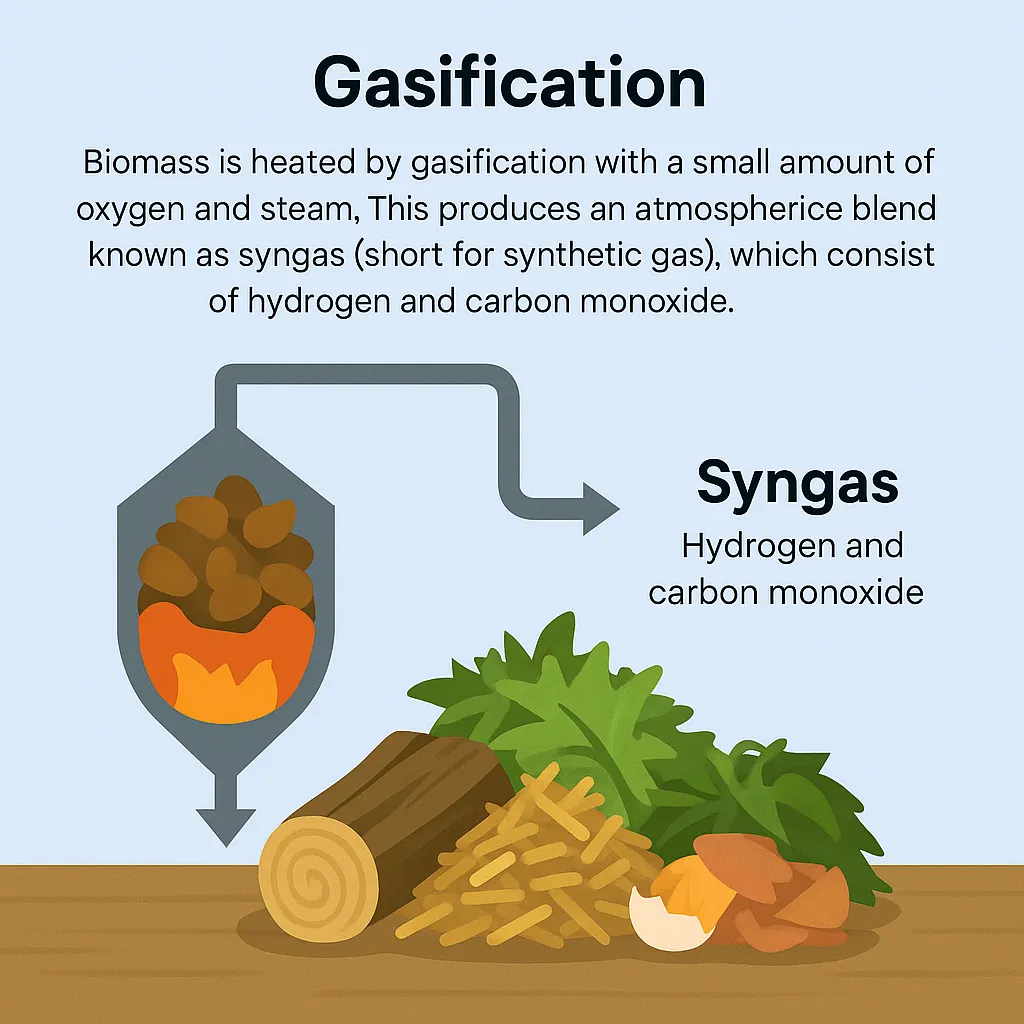
Gasification
Biomass is heated by gasification with a small amount of oxygen and steam. This produces an atmospheric blend known as syngas (short for synthetic gas), which consists of hydrogen and carbon monoxide. Syngas might be used as a cleaner-burning fuel to produce electricity, heat, or even for modified diesel engines.
What About Using Microorganisms?
Another is biochemical conversion. It employs bacteria, yeast, or enzymes to decompose biomass — particularly items high in sugars and starches. These microorganisms, through fermentation, ferment the biomass into ethanol or other biofuels that can be utilized in motors or mixed with gasoline.
It is extensively utilized in the synthesis of bioethanol, particularly from corn and sugarcane.
How Do Chemical Reactions Assist?
Chemical conversion employs chemical reactions to convert biomass into fuels and other products. For example, transesterification of vegetable or animal fats to produce biodiesel is commonly done with alcohol. This produces a fuel that can be used in diesel engines with minor or no adaptation.
Chemical conversion is highly adaptable and can convert low-value feedstocks — such as waste fats and oils — into high-value energy products.
Summary
So, how does biomass energy work? It all comes down to taking organic material and applying heat, microorganisms, or chemical reactions to release the energy trapped within.
Whether it is burned to produce steam or distilled into fuel, biomass is still a versatile and renewable means of meeting our increasing need for energy — particularly when waste materials are utilized as the source. Because biomass energy lowers energy costs while also assisting with waste management, I believe it is worthwhile to take into account.
Posted by Abu Talha
With a background in science at the A-level, Abu Talha has studied subjects including physics, chemistry, mathematics, and biology. Along with his more than 1.5 years of experience in digital marketing, he is passionate about writing about electric vehicles, sustainable energy, and how emerging technologies are influencing the future.

